Laboratory Accreditation and QC
|
Accreditation Procedure by which an authoritative body gives formal recognition that a body or person is competent to carry out specific tasks Accreditation body An organization or agency with the authorized right and authority to inspect a facility and provide written evidence of its compliance (certification) and competence (accreditation) with a standard Audit trail/log An audit trail is a security-relevant chronological record that provide documentary evidence of the sequence of activities that have affected at any time a specific Bika object, e.g. AR or Worksheet Blanks A Sample used for QC, that contains none of the analyte of interest, obtained from inhouse prepared stocks or as certified reference material from suppliers In environmental laboratories, Blanks are also put through the complete pretest Sampling and Preparation workflows a the routine Samples they accompany, to ensue samples are not contaminated before analysis. Any measured-value signal in these Blanks thus are due to contamination Variations, e.g. Ambient, Field and Trip Blanks are used are used to validate different parts of operating procedure by using the same container type as routine samples, travelling with to Sample Points, exposure to ambient conditions on site, preservation, transportation, handling, storage, preparation and analysis CAPA. Corrective and Preventative Actions A system to collect information, analyze it and identify and investigate quality problems, and take appropriate and effective corrective and/or preventive action to prevent their recurrence Continuous Improvement The cornerstone of quality management systems; allows the laboratory to gain insights from setting objectives, monitoring through audit and management review, addressing complaints and nonconformities, and performing client satisfaction surveys. A recurring activity to increase the ability to fulfil requirements. Includes the steps Plan, Do, Check, Act Control Chart A control chart is a line graph that displays a continuous picture of what is happening in production process with respect to time. As such, it is an important tool for statistical process control or quality control. Sciencing.com
As used in control graphs: Central Line, Lower Control Limit, Upper Control Limit, used on a control chart to indicate whether any variation in QC Analyses are natural or caused by a specific event, e.g. Instrument maintenance, new reagent lot CLIA Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments. An United States federal regulatory standards that apply to all clinical laboratory testing performed on humans in the United States, except clinical trials and basic research CSV. Computer System Validation The process of documenting that a computer system meets a set of defined system requirements, to ensure accuracy, reliability, consistent intended performance, and the ability to discern invalid or altered records. It is a critical requirement of electronic record compliance, as described in the FDA 21 CFR 11.10 and EMA Annex 11, Section 4. Ofnisystems.com |
EQA External Quality Assessment system for objectively checking the laboratory performance using an external agency or facility GLP. Good Laboratory Practice GLP refers to a quality system of management controls for research laboratories and organizations to ensure the uniformity, consistency, reliability, reproducibility, quality, and integrity of chemical testing. It is a data quality system, not be confused with laboratory safety standards. Wikipedia.org HIPAA - Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 An act to amend the Internal Revenue Code of 1996 to improve portability and continuity of health insurance coverage, to combat waste, fraud, and abuse in health insurance and health care delivery, to promote the use of medical savings accounts, to improve access to long-term care services and coverage, to simplify the administration of health insurance ISO 17025 Specifies the general requirements for the competence to carry out tests and/or calibrations, including sampling. It covers testing and calibration performed using standard methods, non-standard methods, and laboratory-developed methods ISO 15189 Medical laboratories Requirements for quality and competence. An international standard that specifies the quality management system requirements particular to medical laboratories based on the ISO/IEC 17025, general requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories Includes specifics on collecting patient samples, the interpretation of test results, acceptable turnaround times, how testing is to be provided in a medical emergency, and the lab's role in the education and training of health care staff. Wikipedia.org ISO standards A set of international standards providing guidance for quality in the manufacturing and service industries; developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) to help companies effectively document the quality system elements to be implemented to maintain an efficient quality system
Levy-Jennings chart A a graph plotting QC data to give a visual indication whether a laboratory test is working well. Its x-axis plots time, the y-axis how far away the result is from the mean, which is the expected value for the reference control sample being analysed. Lines across the graph plots the mean, as well as one, two and three standard deviations to either side of the mean. Wikipedia.org METRC. Marijuana Enforcement Tracking Reporting & Compliance A system for tracking state-legalised cannabis in 16 States the USA Metrological Traceability The property of a measurement result whereby the result can be related to a reference through a documented unbroken chain of calibrations, each contributing to the measurement uncertainty. WMO.int OOS Out of Specification OOR Out of Range
|
Proficiency Testing ISO 170 43: Proficiency testing schemes are inter-laboratory comparisons that are organized regularly to assess the performance of analytical laboratories and the competence of the analytical personnel CLSI: A programme in which multiple samples are periodically sent to members of a group of laboratories for analysis and/or identification; whereby each laboratory results are compared with those of other laboratories in the group and/or with an assigned value QA. Quality Assurance Used in Bika terminology to differentiate from QC, the quality control measures carried out by analysts and managers on analysis results QA is periodically carried out by the lab's QA officer on the full batch report of lab observations and results interpretation. After passing QA, a report goes to the lab director to review and publish to the clients as applicable QA often includes external measures, EQA, such as participation in inter-laboratory proficiency testing schemes QC. Quality Control QC refers to the quality control measures carried out by analysts and lab managers on Analysis Results the context of standard reference material QMS. Quality Management System A formalised system that documents processes, procedures, and responsibilities for achieving quality policies and objectives. ASQ.org RPD %. Relative Percent Difference RPD is calculated by dividing the difference between a sample and its duplicate by the average of the two expressed as percentage RSD %. Percentage Relative Standard Deviation The deviation measurement that tells how the different numbers in a data set are scattered around the mean. The standard deviation of a data set divided by the average of the data set as percentage Spikes An actual field sample 'spiked' with a known addition of the target analyte, prior to sample preparation and analysis The % Recovery of the analyte measures the effects of interference caused by the specific sample matrix on the analysis method For a QC Spike, the parent sample is a blank uncontaminated sample matrix (water, soil, sediment, etc) to which a known amount of analyte is added, to create the spike SQC. Statistical Quality Control A modern quality control approach, e.g. Levy-Jennings and control charting, which relies heavily on statistical principles Title 21 CFR Part 11 Title 21 CFR of the Code of Federal Regulations deals with US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) guidelines on electronic records. Part 11 defines under which criteria electronic records and signatures are considered trustworthy, reliable and equivalent to paper records
|

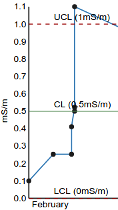 Control Limits. LCL. UCL
Control Limits. LCL. UCL